
- By ACI
- 23 September, 2025
- 6 min Read
EHR vs EMR: Which Should Healthcare Providers Choose?
Healthcare providers face growing pressure to modernize patient care while maintaining compliance and data security. Choosing the right electronic healthcare management suite is critical. Electronic Health Records (EHR) and Electronic Medical Records (EMR) are often confused, yet they serve different purposes. Understanding their differences, benefits, limitations, and integration requirements helps administrators and IT managers make informed decisions.
Defining EMR and EHR
EMR is a digital version of a patient’s chart. It stores medical history, diagnoses, medications, and lab results. EMRs are primarily used within a single healthcare organization.
EHR is more comprehensive. It shares patient information across multiple healthcare settings. EHR includes all EMR data but also supports coordination between specialists, hospitals, and laboratories.
| Feature | EMR | EHR |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Single clinic or practice | Multiple providers and settings |
| Data Sharing | Limited | Extensive, supports interoperability |
| Patient Access | Usually no | Often allows patient portal access |
| Compliance Focus | Internal HIPAA compliance | HIPAA compliance across systems and data exchange |
| Reporting & Analytics | Basic | Advanced, population health insights |
Benefits and Limitations
EMR Benefits
- Fast and familiar for small practices.
- Simple implementation with low upfront cost.
- Useful for internal clinical tracking.
EMR Limitations
- Limited interoperability.
- Cannot easily share patient data outside the organization.
- Less effective for population health management.
EHR Benefits
- Supports seamless patient care across multiple providers.
- Enables advanced analytics and reporting.
- Improves patient engagement through portals and remote monitoring.
EHR Limitations
- Higher implementation cost and complexity.
- Requires staff training and workflow adjustments.
- Integration with legacy systems can be challenging.
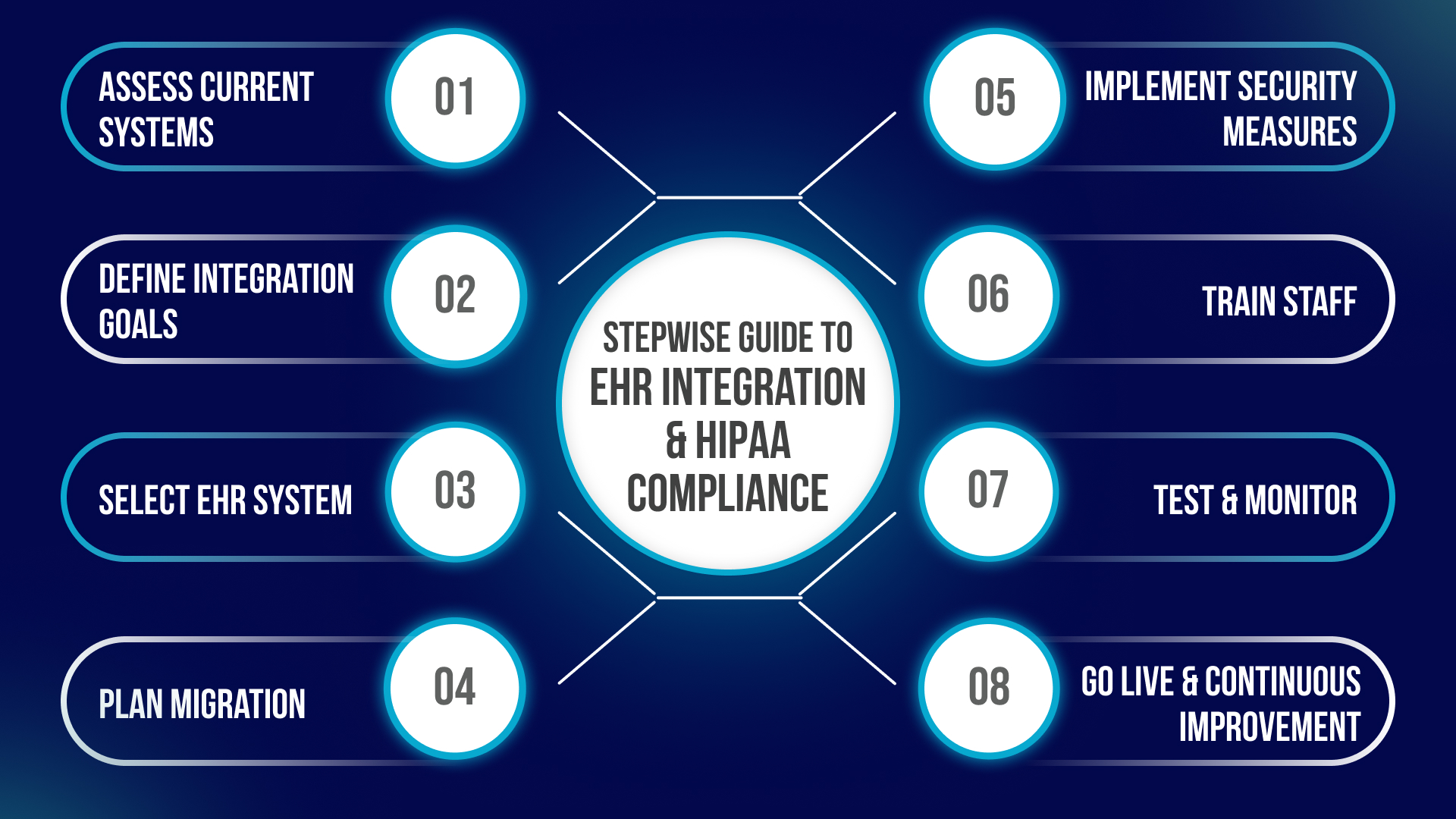
Integration and Interoperability
Integration is a key consideration for 2025 healthcare providers. EHR systems must connect with existing EMRs, lab systems, imaging software, and pharmacy databases. Real-world challenges include:
- Legacy systems that use outdated formats.
- Data migration errors causing incomplete or duplicate records.
- Interoperability gaps when systems do not follow HL7 or FHIR standards.
Successful integration requires careful planning. Hospitals often implement phased migration and continuous testing. Automated validation scripts can reduce errors. Cloud-based EHRs provide better scalability and remote access.
Aryabh Consulting helps healthcare organizations integrate EHRs & EMRs while maintaining HIPAA-compliant workflows. This ensures data integrity, operational efficiency, and regulatory adherence.
HIPAA Compliance and Data Security
Both EMRs and EHRs must comply with HIPAA. Key differences arise in scope and complexity:
- EMRs focus on internal security.
- EHRs require secure data exchange across multiple systems.
Security strategies include:
- Encryption for stored and transmitted data.
- Role-based access controls to limit who can view sensitive information.
- Audit trails to monitor access and changes.
- Regular updates and vulnerability testing to prevent breaches.
Emerging technologies like blockchain and AI-assisted monitoring enhance compliance and security by providing immutable records and detecting unusual access patterns automatically.
Choosing the Right System in 2025
Healthcare administrators should consider:
- Size and scope of the organization. Small clinics may rely on EMR. Large hospitals or networks benefit from EHR.
- Integration needs. Evaluate current software and data formats.
- Patient engagement goals. EHRs support portals and telehealth better.
- Budget and resources. EHRs require higher upfront investment and staff training.
- Compliance strategy. Ensure the system can meet HIPAA requirements across all operations.
A stepwise approach is recommended: assess current capabilities, define data exchange requirements, select a compliant system, and plan for phased integration. Aryabh Consulting offers guidance and technical support to streamline this process without compromising compliance or patient care.
Common FAQs about EMR and EHR
1. What is the main difference between EMR and EHR?
EMR is a digital record used within a single clinic or hospital. EHR includes all EMR data but can be shared across multiple healthcare organizations.
2. Which system is better for large hospitals?
EHR, as it allows seamless data sharing, advanced reporting, and patient engagement across facilities.
3. How does EHR integration impact HIPAA compliance?
EHR integration requires secure data exchange. Compliance depends on encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
4. Can EMR data be migrated to EHR?
Yes, with phased migration, validation tools, and staff training to ensure smooth transition.
5. What are common challenges in EHR adoption?
Legacy systems, staff training, external integration, and maintaining compliance.
6. How do EHRs improve patient care?
By providing a complete medical history across facilities, reducing duplicate tests, and supporting remote care.
7. Are cloud-based EHRs secure?
Yes, if implemented with encryption, access controls, updates, and monitoring.
8. How much does EHR cost compared to EMR?
EHR has higher implementation costs due to broader features, while EMR is simpler and cheaper for small practices.
Conclusion
EMR and EHR serve different but complementary purposes. EMR is ideal for internal record management. EHR supports broader data sharing, analytics, and patient engagement. Choosing the right system requires careful assessment of organizational needs, technical readiness, and compliance obligations. Proper integration and security planning ensure a smooth transition and long-term benefits.
Investing in the right system improves patient care, enhances operational efficiency, and ensures compliance in 2025 and beyond.

