

- By ACI
- 16 December, 2025
- 10 min Read
Understanding the 7 Key Components of IT Infrastructure Management
For business and organizational decision makers, technology infrastructure is no longer a background utility. It is a core operational asset that affects continuity, security, customer experience, and long term growth. As organizations expand across locations, adopt cloud services, and automate business processes, the need for disciplined IT infrastructure management becomes unavoidable.
IT infrastructure management refers to the coordinated oversight of hardware, software, networks, data, cloud environments, security controls, and the people and processes that keep these elements reliable. When managed well, infrastructure supports strategic objectives. When neglected, it introduces risk, downtime, and cost uncertainty.
This article explains the seven key components of IT infrastructure management, how they work together, and why the role of IT infrastructure management is central to modern enterprises. It also outlines how organizations are using automation and AI in IT infrastructure management to improve visibility, resilience, and decision making.
What IT Infrastructure Management Means for Modern Organizations
IT infrastructure management is the practice of maintaining and optimizing the systems that run daily operations. It goes beyond basic technical support. It includes planning, governance, monitoring, security, and continuous improvement across the entire technology stack.
For decision makers, effective IT infrastructure management delivers three outcomes. Stability through consistent system availability. Security through controlled access and risk reduction. Agility through scalable platforms that support new initiatives without disruption.
Without a structured approach, infrastructure becomes fragmented. Teams rely on reactive fixes. Visibility is limited. Costs increase as systems age without clear lifecycle planning. This is why many organizations now treat infrastructure management as a strategic discipline rather than a purely technical function.
The 7 Key Components of IT Infrastructure Management
1. Hardware Platforms
Hardware platforms form the physical foundation of the IT environment. This includes servers, desktops, laptops, storage devices, and networking equipment such as routers and switches. While many workloads have moved to the cloud, physical hardware remains critical in offices, data centers, and hybrid environments.
Effective IT infrastructure management ensures hardware assets are tracked, maintained, and replaced based on usage and risk. Capacity planning prevents performance bottlenecks. Redundancy reduces downtime. Clear lifecycle policies help organizations avoid unexpected failures that disrupt business operations.
2. Software Platforms
Software platforms include operating systems, middleware, and enterprise applications that support business functions. Examples include Windows or Linux environments, database systems, ERP platforms, and collaboration tools.
Managing software platforms requires consistent patching, version control, and compatibility planning. Outdated software introduces security vulnerabilities and operational risk. Strong IT infrastructure management aligns software platforms with business workflows so systems support how teams actually work rather than forcing inefficient workarounds.
3. Network Infrastructure
Network infrastructure connects users, systems, and data across locations. It includes wired and wireless networks, firewalls, gateways, and internet connectivity. Network reliability directly affects productivity, application performance, and security posture.
From an infrastructure management perspective, networks must be monitored continuously. Bandwidth usage, latency, and access patterns need visibility. Secure segmentation and controlled access reduce exposure to threats. As organizations adopt remote and hybrid work models, network infrastructure becomes even more central to daily operations.
4. Data Storage and Management
Data is one of the most valuable assets an organization owns. Data storage and management covers databases, file systems, backups, and recovery mechanisms across on premise and cloud environments.
Strong IT infrastructure management ensures data is accessible, protected, and recoverable. Backup strategies are tested regularly. Storage capacity is planned based on growth trends. Governance controls define who can access sensitive information. Poor data management increases the risk of loss, regulatory exposure, and operational disruption.
5. Cloud Services
Cloud services have become a core component of modern infrastructure. Organizations use public, private, or hybrid cloud environments to host applications, store data, and scale resources on demand.
Managing cloud services requires discipline. Cost visibility, workload performance, security controls, and integration with on premise systems must be actively governed. Effective IT infrastructure management treats cloud environments as part of a unified ecosystem rather than isolated platforms.
For decision makers, the value of cloud adoption depends on how well these environments are managed over time. Without oversight, cloud complexity and cost can grow quickly.
6. Security
Security spans every layer of the infrastructure. It includes firewalls, endpoint protection, identity and access controls, monitoring tools, and security policies. As threat activity increases across industries, security can no longer be treated as an afterthought.
The role of IT infrastructure management includes embedding security into daily operations. Access is granted based on role. Systems are monitored for unusual activity. Vulnerabilities are addressed through structured processes. A strong security posture protects not only systems but also business reputation and trust.
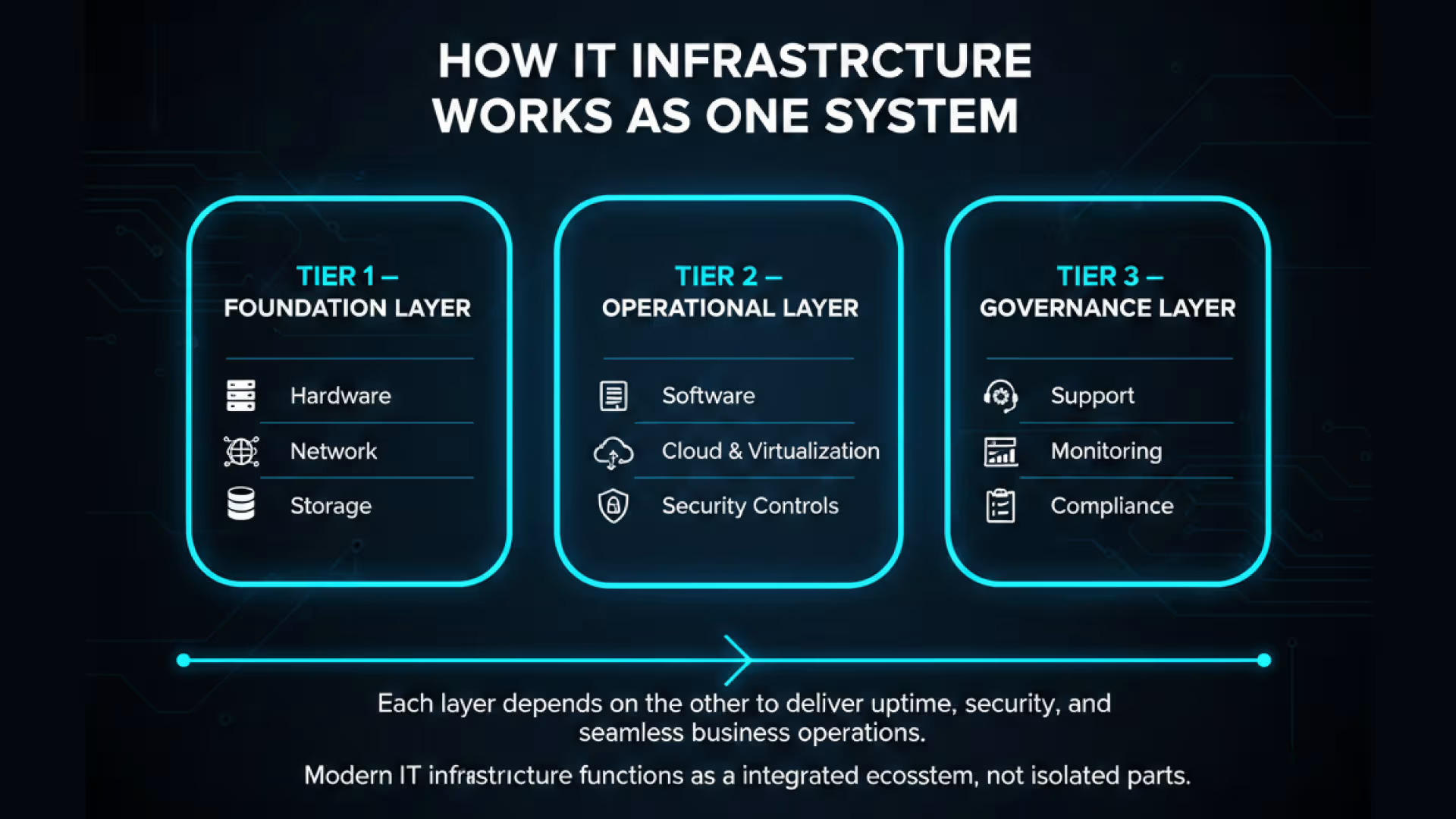
IT Service Management People and Processes
Technology does not manage itself. IT service management represents the people and processes responsible for operating the infrastructure. This includes service desks, incident response, change management, disaster recovery planning, and ongoing optimization.
Well defined processes reduce downtime and confusion during incidents. Clear ownership ensures accountability. For decision makers, this component often determines whether infrastructure investments deliver long term value or degrade over time.
Management Focus Areas That Sustain Infrastructure Performance
1. Monitoring and Maintenance
Continuous monitoring is a cornerstone of IT infrastructure management. Proactive checks identify issues before they affect users. Performance metrics provide insight into capacity trends. Preventive maintenance reduces the likelihood of unplanned outages.
Organizations that invest in monitoring gain predictability. They can plan upgrades, allocate budgets, and support growth with fewer disruptions.
2. Security and Business Continuity
Infrastructure resilience depends on preparation. Business continuity planning ensures systems can recover from failures, cyber incidents, or natural disruptions. Backup and recovery processes are tested regularly. Failover mechanisms are documented and understood.
This focus area highlights the role of IT infrastructure management in protecting revenue and operations during unexpected events.
3. Automation and Intelligent Operations
Automation reduces manual effort and improves consistency across infrastructure tasks. Routine activities such as provisioning, patching, and configuration management can be automated to reduce error and response time.
Many organizations are now introducing AI in IT infrastructure management. AI driven tools analyze logs, detect anomalies, predict capacity needs, and prioritize incidents. This does not replace human oversight. It augments decision making and allows IT teams to focus on higher value initiatives.
4. The Strategic Role of IT Infrastructure Management
For business leaders, the role of IT infrastructure management extends beyond uptime. It supports scalability, compliance, and innovation. Infrastructure decisions affect how quickly new services can be launched, how securely data is handled, and how efficiently teams collaborate.
When infrastructure is managed as a cohesive system, organizations gain control. They reduce technical debt. They improve planning accuracy. They align technology investments with business priorities.
This strategic role becomes even more important as organizations adopt automation, integrate external partners, and rely on data driven decision making.
Why Organizations Partner With Aryabh Consulting
Aryabh Consulting Inc. approaches IT infrastructure management as a long term enterprise responsibility rather than a one time implementation. Our focus is on building user centric, scalable systems that support real business operations.
As an authoritative enterprise software management provider, Aryabh Consulting helps organizations design, manage, and optimize infrastructure across hardware, software, cloud, and security layers. We emphasize clarity, governance, and operational discipline.
What differentiates our approach is post care. We provide ongoing monitoring and optimization, long term support, and SLA driven maintenance. Infrastructure environments evolve. Our engagement model ensures systems continue to perform as business needs change.
For decision makers seeking a reliable enterprise partner, Aryabh Consulting delivers structure, accountability, and sustained value.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is IT infrastructure management in simple terms
IT infrastructure management is the practice of managing the hardware, software, networks, data, and cloud systems that support daily business operations. It ensures these components work together reliably, securely, and efficiently.
2. Why is IT infrastructure management important for decision makers
For decision makers, IT infrastructure management reduces operational risk, improves system availability, and provides better cost control. It directly supports business continuity, compliance, and long term scalability.
3. What is the role of IT infrastructure management in business growth
The role of IT infrastructure management is to create a stable foundation that allows organizations to scale operations, adopt new technologies, and respond quickly to market changes without disruption.
4. How does AI help in IT infrastructure management
AI in IT infrastructure management helps analyze system data, detect anomalies, predict capacity needs, and prioritize incidents. It improves visibility and decision making while reducing manual effort.
5. What are the biggest challenges in managing IT infrastructure
Common challenges include legacy systems, limited visibility, security risks, rising cloud costs, and reactive maintenance. These issues often arise when infrastructure lacks standardization and continuous oversight.
6. How does ongoing monitoring and support improve infrastructure performance
Ongoing monitoring and SLA driven support help identify issues early, optimize performance, and maintain system reliability over time. Continuous optimization ensures infrastructure continues to align with evolving business needs.





